Table of Contents
Establishing and Running A Nonprofit
- Nonprofit Law and Consultation
- Amy Hereford – JD, JCD/PhD
- 6400 Minnesota Ave – Saint Louis, MO 63111
- 314-972-4763 – amyhereford@gmail.com
Introduction
- Research and Planning
- Assemble Resources
- Establish Legal Foundations
- Establish Financial Systems
- Establish Compliance Systems
- Establish Communications & Development
- Find a Site and Begin Operations
- Business Plan – Executive Summary
Business Plan
- The Mission Statement
- Important dates in beginning the business
- Names and roles of founders, key employees
- Location and description of site
- Description of services
- Funding sources
- Market highlights
- Strategic Development Plan for 1, 3, 5 years
Business Plan - Needs Analysis
- Define Market Segment
- Clearly define client/customer base
- How many potential clients are there?
- Where are they found?
- What are their characteristics?
- Identify other players
- Others providing similar services
- Others serving the same client base
- Similar service providers in other regions
n-2-n Neighbor to Neighbor
- Needs: Many of our elderly residents need simple assistance in their homes, cleaning, shopping, yardwork, etc. Some also need simple companionship and primary caregivers need respite assistance. Others with handicaps or temporary medical needs may also benefit.
- Scope of Need: In our town of 30,000, we estimate 1,500 households would benefit from some sort of assistance.
- Mission and Goals: Connecting neighbors with neighbors and lending a helping hand to elders.
Business Plan – Organization Description
- Overview of organization’s plan to meet the needs identified above
- Identify goods and services and describe how they will be provided
- Organization and Management
- Board Roles and Responsibilities
- Organizational Chart & Job Descriptions
Business Plan – Communication and Development
- Communication
- Create communication plan
- Develop methods of maintaining contact with
- Clients and potential clients
- Grantors and donors and supporters
- Development
- Create development plan
- Identify sources of funding
- Identify development strategies to engage the community
Business Plan – Financials
- Financial Statements to Date
- Budget for start-up
- 3 months
- 6 months
- 1 year
- 2 years
- 3 years
Business Plan – Appendices
- Resumes of key managers
- List of Services
- Letters of reference
- Details of market studies / needs analysis
- Relevant bibliography
- Legal documents
- Articles, Bylaws, Corporate Minutes
- Copies of leases; Building permits; Contracts
- Licenses, Insurance, etc.
- List of business consultants and professionals
Budget
| Account | Startup | Year I | Year II |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contributions | $1000 | $500 | $500 |
| Grants | $1000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Membership Dues | . | . | . |
| Investment Income | . | . | . |
| Govt services w/o charge | . | . | . |
| Other Revenue | . | . | . |
| Subtotal | $2000 | $10,500 | $10,500 |
| Program Service Revenue | $2000 | $15,000 | $30,000 |
| Total 8-9 | $4000 | $25,500 | $40,500 |
| Capital Gains/Losses | . | . | . |
Assemble Resources
- Based on Research and Planning
- Board Members
- Management
- Staff
- Funding & Resources
- Initial
- Development Plan
Crowdfunding
- Internet-facilitated fundraising
- Tax Laws still apply
- Charitable Solicitation Laws still apply
- Take account of costs and fees (3-15%)
- Equity, Loan, Gift
- Entrepreneur: wider exposure, risk loss of ideas or control
- Investor: many ideas, lack of due diligence
Establish the Legal Foundations
- Increasing burden of inter-related legal regulation
- Cost of these mistakes
- An attorney familiar with nonprofit law is an indispensable help in successfully meeting all these demands
- File Articles of Incorporation and draft Bylaws.
- Apply for Federal Tax ID number and Federal Tax Exempt status. FREE
| Articles of Incorporation | Bylaws | EIN SS-4 | Tax Exemption Form 1023 |
- Establish a Conflict of Interest Policy
- Develop a Corporate record-keeping system
- File for state and local tax exemption
- Fulfill charitable solicitation law requirements
- Apply for a nonprofit mailing permit
- Obtain necessary business licenses and permits, professional licenses and insurance
- Comply with zoning laws and municipal regulations
- Comply with employment laws and establish payroll tax withholding
- Protect trademarks / tradenames & intellectual property
- Develop a checklist for Corporate Legal Compliance
Articles of Incorporation and Bylaws
- Articles of Incorporation
- Gives the organization a separate legal existence
- Filed with Secretary of State
- Generally a fill in form, but care must be taken in drafting purpose clauses
- Purpose and Dissolution - required language: https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/suggested-language-for-corporations-and-associations
—-
Bylaws
- Internal regulation of the organization
- Governance: Members and Directors
- Appointment of Officers and Directors
- Role and responsibilities of the Board
- Meaningful oversight of staff – purposes, activities, financials
- Amendment and Dissolution - repeat required lanuage regarding purpose and dissolution.
Tax ID number
- EIN
- Form SS-4
- Easy Application
- Needed for
- Bank account
- Tax exempt filing
- Employment taxes
Federal Tax Exemption Application
Form 1023
- Part I Identification of Applicant
- Part II Organizational Structure
- Part III Required Provisions of Organizing Documents
- Part IV Narrative of Activities
- Part V Compensation of Officers / Directors / Key Employees
- Part VI Beneficiaries of the Organization
- Part VII History
- Part VIII Specific Activities
- Part IX Financial Data
- Part X Public Charity Status
- Part XI User Fee
- Supporting Schedules
Form 1023-EZ
- Form introduced 2014
- Simplified application process for smaller organizations
- Only 3 pages long!
- Reduced application backlog
Form 1023-EZ
- requires organizations to:
- Certify that organizing document complies with 501c3
- Certify that organization will not engage in prohibited activities
- Provide names/addresses of officers/directors
- Remember: Approved Forms 1023-EZ are open to public inspection
- Don’t Forget to Pay the User Fee!
| Application Type | User Fee |
| Form 1023 | $600 |
| Form 1023-EZ | $275 |
| Group exemption letter | $2,000 |
- Must be paid through www.pay.gov
- Approval of your application is not guaranteed
- Be sure to fill out the application completely and correctly
- Once application is approved, IRS will mail a determination letter to the organization
Form 1023-EZ
- for smaller organizations seeking 501c3 status who do not have any of the following characteristics:
- Annual gross receipts >$50k
- Total assets >$250,000
- Foreign orgs, Organizations with ties to terrorism
- LLCs
- Successors to for-profit orgs
- Previously revoked
- Churches, Schools, Hospitals
- Supporting Orgs, credit counseling, carbon credits, HMO, ACO, donor advised funds, Private foundations, etc….
Reduction in 'Inventory'
- Reduced cases more than 270 days old by 91%
- From 54,564 (in 4/14) to 4,791 (in 9/14)
- Average from nearly 2 years to 30 days on 1023EZ
Form 990
- Annual IRS reporting form for Exempt Organizations
- Provides information on the filing organization's mission, programs, and finances.
- No tax is due on organization's exempt mission
- Tax due on Unrelated Business Income – reported on Form 990-T
- Information Return
- 990 & 990-EZ https://efile.form990.org/
| 990-N | Gross receipts normally ≤ $50,000 (may file 990-EZ or 990) |
| 990-EZ | Gross receipts < $200,000, and Total assets < $500,000 (may file 990) |
| 990– | Gross receipts ≥ $200,000, or Total assets ≥ $500,000 |
| 990-PF | Private foundation - regardless of financial status |
Ethics
Establish a Conflict of Interest Policy
- Define Interested Persons
- Anyone who stands to benefit from a decision
- Require disclosure
- Remaining decisionmakers vote on conflict
- Record proceedings
- Responding to violations
- Education and periodic review
Nonprofit Ethics
- Provide meaningful financial oversight by board
- Financial literacy training for board members
- Audit Committee separate from finance committee
- Rotate Auditors every 5 years
- Establish Document Management Policy
- Review corporate bylaws
- Review duty of care
- Review other corporate compliance obligations
- Review intermediate sanctions
Develop a Corporate Record-keeping System
- Records System
- Board, Management and Staff Records
- Finanical records
- Management
- Compliance (tax, grants, etc)
- Record Creation and Use
- Access and confidentiality
- Storage
- Security
- Record Retention and Destruction
- Legal implications
- When and How
Donation Receipts
State and Local Requirements
- Income Tax Exemption (state)
- Sales Tax Exemption (state and local)
- Property Tax Exemption (local)
- Franchise Tax, etc. (state and local)
State charitable solicitation requirements
- Soliciting funds from the general public
- Fee for service and grant monies generally not covered
- Vary from one jurisdiction to another
- Check state websites:
- Secretary of State, Department of Revenue, Attorney General
Missouri
- Articles of Incorporation (SOS)
- Apply for sales tax exemption from the state (DOR)
- Missouri Sales/Use Tax Exemption Application (Form 1746 Rev. 10-98)
- Need your IRS Determination letter – 501c
- Register as a charity (AG)
- Annual Report (SOS) (AG)
Apply for a nonprofit mailing permit
- Eligible organizations: Religious, Educational, Scientific, Philanthropic (Charitable), Agricultural, Labor, Veterans, Fraternal
- Detailed regulations and qualifications
- Many organizations use e-mail newsletters instead
- ConstantContact, MailChimp, VerticalResponse
- Email Groups
Local Regulatory Issues
- Business licenses and permits
- Licensing and insurance of professionals
- Business license
- Check Secretary of State website
- Zoning laws and municipal regulations
- Check city, county, municipal offices for necessary permits, regulations, zoning issues.
Employment and Payroll
- Federal Employment Laws
- State Employment Laws
- Industry Employment Requirements
- Payroll
- Exempt vs Nonexempt Employees and Overtime
- Withholding Accounting and Payment
- Employment Handbook
Intellectual Property
- Offensive and Defensive
- Trademark exclusively identifies the source or origin of products or services
- Copyright is a set of exclusive rights regulating the use of a particular expression of an idea or information
- Patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by a state for a fixed period of time which is new and useful
Checklist for Corporate Legal Compliance
- Board Meetings and Minutes
- Annual Filings
- Federal Tax – 990
- State Corporate filings / Charitable filings
- Permits, licenses
- Financial and Audit Requirements
- Grant Applications and Reports
- Employment
- Contracts and Insurance
Policies and Procedures
- Staff Policies and Procedures
- Staff Record Management Policies and Procedures
- Staff Budget and Financial Policies and Procedures
- Employment Policies
- Staff Training Policies
- Client Services Policies and Procedures
- Character of Policies and Procedures
- Clear, useable and available to staff
- Managerial and organizational
- Drafted to anticipate and prevent legal problems.
Establish Financial Systems
- Develop an accounting system and budget.
- Gone are the days of shoe box accounting.
- Professional help in this area is important.
- Board Financial Management must ensure appropriate
- Oversight, recordkeeping and reporting.
Communications & Development
- Printed materials, Website, E-mail addresses, Media Relations
- Database:
- Create development plan
Find a Site and Plan to Begin Operations
- All the hard work begins to pay off in services offered to clients.
- Ensure Policy / Procedures Compliance
- Ensure Recordkeeping
- Regularly review operations
- Update policies and procedures as required
Further Resources
- Email amyhereford@gmail.com for more information
6 reasons NOT to set up a Nonprofit
- 1. There is already an organization filling that need.
- 2. You do not have other people “on board” yet.
- 3. Your idea is better suited as a for-profit enterprise
- 4. Starting up takes time.
- 5. You’d like to plan a one time fundraiser.
- 6. Your type of cause makes it difficult to secure long term funding.
Dissolution
- Meet and/or extinguish all outstanding claims against the organization
- Send Articles of Dissolution to Secretary of State
- Required approval: Directors
- Higher standards for approval may be found in the Articles or Bylaws
- Send Notice to Attorney General
- Notice of who received assets of the Nonprofit
- Retain enough to pay any outstanding debts and professional fee
- Send Notices to claimants
- Mail notice to known claimants
- Publish notice for unknown claimants
- Obtain Tax Clearance Letter from Dept of Revenue
- Send Articles of Termination to Secretary of State
- Mail with Tax Clearance Letter
- Once all business is complete
Part II
What is a non-profit?
- An organization is not organized for profit
- Organized
- under the state nonprofit statute
- for a recognized nonprofit purpose, e.g. religious, charitable or educational
- Often exempt from federal and state taxes: a tax exempt organization – if it complies with certain requirements
- Church, Hospital, University, Soup kitchen, Little League, Foundation
Tax-Exempt Organization Reference Chart

Public Charity
- Inherently public charities: Churches, Schools, Hospitals
Public Charity
- Supporting Organizations:
- 509a3 – Type I: Subsidiary
- 509a3 – Type II: Overlapping Governance or Contracts
- 509a3 – Type III: Functionally Integrated or Grants
- Private Operating Foundation – devotes most of its revenues to carrying out its exempt purposes.
What is a Nonprofit Board?
- Governing body of the organization
- Acts as president, congress and supreme court
- Does not own, but administers the organization, its programs and its assets in the public interest
- Responsible to the members, beneficiaries of services, state attorney general, general public
- Has the responsibilities specified in the Articles and Bylaws
What is a Church Sponsored Organization?
- An organization with a split personality
- Organized under church law with church responsibilities
- Organized under civil law with civil responsibilities
- Two bodies of law, Two sets of responsibilities, Two lines of oversight
- Understand how it is organized, and how it is operated
Legal Duties
- Duty of Care: Take reasonable care when making decisions for the organization, be competent
- Duty of Loyalty: Act in the best interest of the organization, confidentiality
- Recusal: Stand aside when there is a conflict of interest
- Duty of Obedience: Act in accordance with the organization’s mission, public trust
Articles of Incorporation
- Agreement with the state to establish and maintain the corporation: name, duration, location, registered agent, purpose, nonprofit status, amendment & dissolution
- Regular filing responsibilities, often overseen by secretary or treasurer
Bylaws
- Law for the Corporation
- Board Governance
- Purpose
- Board qualifications, terms and succession
- Board powers and responsibilities
- Meetings, notice, decisionmaking
- Reporting requirements
- Financial structure
- Officers qualifications, terms and succession
- Committees
- Amendment and dissolution
Types of Boards
- Two – Tiered Board: Member / Director
- Governing Board
- Standard board, governance, oversight
- Operating Board
- Standard board, governance, oversight
- Board also has responsibilities in the organization:
- Fundraising and Donation (give, get, get off)
- Volunteering
- Operations
- Working Committees
- Expectations
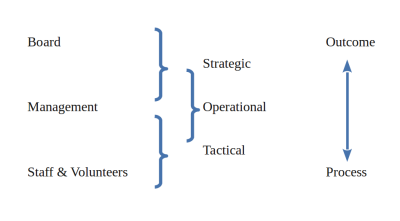
Traditional Nonprofit Organization Structure

Key Board Responsibilities
- To make sure that critical systems are functioning the way they should
- To make sure that effective systems of checks and balances are in place
- To ask the right questions when clues and information tells us that something is not right
Board Requirements
- File and publish Form 990 and State filings
- Audit / review – file if necessary
- Keep state filings current
- Licensing and credentialing, JCAHO, HIPAA, EMTALA, Stark Laws
- Report UBIT and pay taxes
- Pay employment taxes and comply with employment laws, including: ADA, OSHA, FLSA, FICA, COBRA, FMLA.
- Limited Lobbying, avoid Campaigning
- Give receipts to donors for contributions above $250.
- Collect sales tax
- Get court approval for distribution of assets.
- Register for charitable solicitation and gaming
- Pay property tax or obtain exemption
- Comply with mailing laws and bulk mailing laws
- Meet terms of conditional donations
- Comply with state law regarding conflicts of interest.
- Register professional fundraising
- Obtain business permits
- Record minutes of board and annual meeting.
Liability
Wrongful Action
- Of corporation – corporation responds for actions of the corporation
- Of employee
- Corporation responds under respondeat superior doctrine
- Employee responds if outside scope of work
- Of board member
- Corporation responds if director was reasonably prudent
- Board member responds if there is a failure of duty of care, loyalty or obedience
Fiscal Sponsorship and Partnerships
What is Fiscal Sponsorship?
- An arrangement between a 501c3 public charity and a project in which, typically, the charity receives and expends funds to advance the project while retaining discretion and control over the funds.
- Not Fiscal Agency – Wrong Term
- charity is not agent to receive project $
- Fiscal Sponsorship – Preferred Term
- charity directs, controls project $
Two Main Ways to Do It Right
- Direct Project Model (A)
- Independent Contractor is Model B
- Pre-Approved Grant Model (C)
Direct Project, Model A
- Project belongs to sponsor
- Project is not a separate legal entity
- Project personnel are employees / volunteers
- Contributions belong to sponsor
Direct Project, Model A
- Sponsor is liable for everything
- Sponsor reports revenue and expenses
- Sponsor OWNS project
- Project may have advisory committee
Legal Steps
- Project director or advisory committee establishes a contract with sponsor.
- Sponsor’s board has already approved a sponsorship program or approves now.
- Fundraising done in name of sponsor.
- Sponsor receives grants, donations into project fund account, pays costs directly.
Pre-Approved Grant, Model C
- Project belongs to grantee
- Project is in a separate legal entity
- Project personnel work for grantee
- Charitable contributions go to sponsor first
Pre-Approved Grant, Model C
- Grantee is liable for project
- Sponsor reports contributions in and grants out
- Grantee reports grant in and expenses out
- Sponsor retains “variance power” (discretion and control) over funds
Pre-Approved Grant – 7 Steps
- Written grant proposal from project
- Sponsor evaluation of proposal
- Sponsor Board approval
- Written grant agreement
- Proper solicitation of funds
- Proper accounting for funds
- Reports from grantee to sponsor
How Could Anything Go Wrong?
Problems Common to Both Models
- Sponsor is “absent,” or “We are just using their 501c3”
- No written agreement
- Confusion with DAF or other programs
- Sponsor mischaracterizes relationship
- Donor confusion about recipient
Pre-Approved Grant Problems
- Failure to pre-approve the grant relationship
- Grantee fails to report income
- Ownership of intellectual property
- Grantee fails to report back to sponsor
- Sponsor pays grantee’s bills directly
- Lack of professional grants management
Resources
- Fiscal Sponsorship: 6 Ways To Do It Right, 2005 edition
- Resources
- Fiscal Sponsorship: 6 Ways To Do It Right, 2005 edition
- National Network of Fiscal Sponsors:
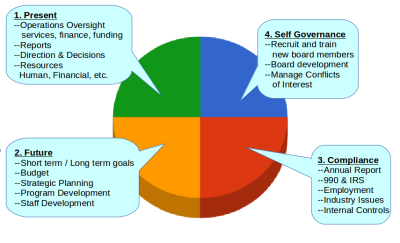
Basic Nonprofit Board Responsibilities
1. Mission and Purpose
- Ensure the organization’s mission and purpose.
- Create and review a statement of mission and purpose
- Articulate the organization’s goals, means, and primary constituents served
2. Select Executive
- Hire the chief executive
- Outline executive's responsibilities
- Evaluate and or Fire
3. Financial Oversight
- Meaningful financial oversight.
- Annual Budget and Audit / review
- Ensuring that proper financial controls are in place
4. Resources
- Ensure adequate resources
- Enable the organization to fulfill its mission.
5. Legal and Ethical Integrity
- Ensure legal compliance and ethical integrity
- Maintain accountability
- Know and adhere to legal standards and ethical norms.
- Comply with tax reporting responsibilites
6. Planning
- Ensure effective organizational planning.
- Actively participate in an overall planning process
- Assist in implementation
- Monitor the progress.
7. Board Development
- Recruit and orient new board members
- Assess board performance
- Articulate prerequisites for candidates
- Evaluate its own performance
- Ensure leadership succession
8. Public Image
- Enhance the organization’s public standing
- Clearly articulate the organization’s mission, accomplishments, and goals to the public
- Garner public support
9. Programs
- Determine, monitor, and strengthen the organization’s programs and services
- Evaluate programs for consistency with the organization’s mission
- Monitor effectiveness
10. Support Operations
- Support the chief executive and assess his or her performance
- Ensure that the chief executive has the support needed to further the goals of the organization
- Don't micromanage
- Don't rubber-stamp
- Balanced, meaningful oversight
IRS Priorities
- Nonexempt purpose – organizational / operational »Revocation
- Exempt asset protection – self-dealing, excess benefit transactions, loans to disqualified persons »Fines
- Tax gap – employment taxes, UBIT
- International – foreign grants, FBAR
- Employee / Independent Contractor
NonProfit Governance
Common Mistakes
1. Failing to Understand Fiduciary Duties
- Duties of obedience, due care and loyalty.
- Potential liability
- Increased scrutiny from the I.R.S., etc.
2. Failing to Provide Effective Oversight
- Boards can delegate
- Must exercise oversight
- Policies / Procedures – that are followed
- Review of 990, and Financials
- Review of Policies
- Conflict of interest, Executive compensation, Travel and expense, Whistleblower, Employment
- Committees
3. Deference to the Executive, Chair or Founder
- No one can replace board supervision
- Executive Committee
- Board Chair
4. Micro-managing Staff
- Keys, staff reports
- Strategy and direction
- Resist personal interest, and staff complaints
5. Avoiding The Hard Questions
- Ask the tough questions
- Air differences
- Valuable board members calmly and respectfully, speak their mind
- Open, vigorous discussions
6. Insufficient Conflict of Interest Management
- Have a policy
- Discuss it periodically, when might it arise
- Know procedure of disclosure and decisionmaking
- Document
7. Lack of Awareness of Governing Law
- For profit directors must adjust
- Understand requirements and penalties for non-compliance
- Ongoing board training
8. Outdated, Inconsistent Governing Documents
- Know the documents
- Read and apply the documents
- When a governance question arises know how to find the answer in the documents
- Review documents for consistency, law change, operational change
- Slack
9. Airing Disagreements Outside the Boardroom
- “What happens in the boardroom stays in the boardroom.”
- Duty of loyalty
- Don't publicize disagreement with board decision.
- If it is too egregious, resign
- If it is unlawful, consider legal action to protect the organization's rights
10. Failure to Cultivate Board Diversity
- Family and friends of the organization
- Volunteers and clients, alum
- Community leaders
- Professionals
- Skills
- Reflect population served
Top 10 Nonprofit Risks
Risk 1: Financial loss
- To prevent this, it helps to have a well-trained, well-informed board.
Risk 2: Social Media
- Exposures from social media use, misuse and naivete.
- Risk-management strategies include written guidelines for employees, volunteers and members and a point person to monitor social media.
Risk 3: Incivility
- Investigate complaints without delay and hold staff and volunteers accountable.
Risk 4: Form 990
- IRS Form 990 and federal tax-exempt status.
- Losing that status is really easy.
Risk 5: Copyrights
- Copyrights and trademarks. Use the copyright symbol.
- Use work-for-hire agreements with contractors.
- Respect the work of others.
Risk 6: Contracts
- Failure to limit a contracting authority and other common mistakes in contracting.
- Develop a simple policy, clarify who has authority to enter one and obtain legal review, before signing.
Risk 7: Lack of Consistency
- Lack of synchronicity in board policy and practice.
- Look at policies. Do they need changing?
Risk 8: Conflicts of Interest
- Failure to understand and manage conflicts of interest.
- Failure to have a policy
- Make sure the policy is easily understood.
Risk 9: Fraud
- Understand the inherent risks and fraud schemes.
Risk 10: Reputation
- Remember humility (admit mistakes) and speed (without delay).
Caught in the Act - - - Again
Parting Words
- Board composition and numbers matter; guard against founder's syndrome
- Policies are important but must be understood, implemented and enforced
- Public perception is critical - be careful of conflicts of interest and sweetheart transactions, even if they are not unlawful - be responsive
- Communications responding to crises that are only CYA pieces will not fool the public
- Delegate, but only with due care and proper oversight (e.g., reporting)
- Outside assistance can be invaluable (e.g., audits, legal opinions, investigations)
- Review key communications, including their websites and the Form 990