Table of Contents
Small Business: Legal Issues
- Nonprofit Law and Consultation
- Amy Hereford – JD, PhD
- 6400 Minnesota Ave – Saint Louis, MO 63111
- 314-972-4763 – amyhereford@gmail.com
Introduction
- Research and Planning
- Assemble Resources
- Establish Legal Foundations
- Establish Financial Systems
- Establish Compliance Systems
- Establish Communications & Development
- Find a Site and Begin Operations
- Business Plan – Executive Summary
Entrepreneurship
- Rewards
- Profit - Freedom from the limits of standardized pay for standardized work.
- Independence - Freedom from supervision and the rules of bureaucratic organizations.
- Satisfying Way of Life - Freedom from routine, boring, unchallenging jobs.
- Risks
- Uncertainty of income
- Risk of losing entire investment
- Long hours and hard work
- Lower quality of life until the business gets established
- Complete responsibility
- Success
- Passion
- Persistence
- High need for achievement
- Willingness to take measured risks
- Confidence and self-reliance
- High energy level
- Desire for responsibility
- Routes to Small Business
- Startup
- Buyout
- Franchising
- Family Business
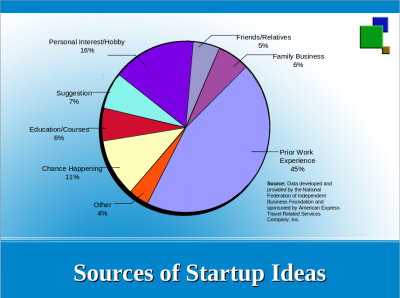
- Ideas for New Businesses
- New Market: Providing customers with a product/ service that is not in their market but already exists elsewhere.
- New Technology: Using a new technical process that provides the basis for new product or service ideas.
- New Benefit: Performing an old function for customers but in a new and improved way.
Business Plan
- The Mission Statement
- Important dates in beginning the business
- Names and roles of founders, key employees
- Location and description of site
- Description of services
- Funding sources
- Market highlights
- Strategic Development Plan for 1, 3, 5 years
Business Plan - Needs Analysis
- Define Market Segment
- Clearly define client/customer base
- How many potential clients are there?
- Where are they found?
- What are their characteristics?
- Identify other players
- Others providing similar services
- Others serving the same client base
- Similar service providers in other regions
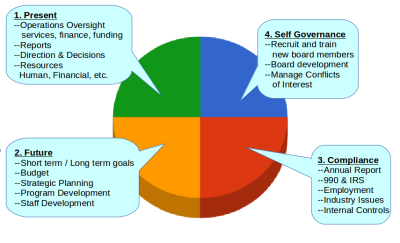
Business Plan – Organization Description
- Overview of organization’s plan to meet the needs identified above
- Identify goods and services and describe how they will be provided
- Organization and Management
- Board Roles and Responsibilities
- Organizational Chart & Job Descriptions
Business Plan – Communication and Development
- Communication
- Create communication plan
- Develop methods of maintaining contact with
- Clients and potential clients
- Grantors and donors and supporters
- Financing
- Create Financing plan
- Identify sources of funding
- Identify development strategies to engage the community
Business Plan – Financials
- Financial Statements to Date
- Budget for start-up
- 3 months
- 6 months
- 1 year
- 2 years
- 3 years
Business Plan – Appendices
- Resumes of key managers
- List of Services
- Letters of reference
- Details of market studies / needs analysis
- Relevant bibliography
- Legal documents
- Articles, Bylaws, Corporate Minutes
- Copies of leases; Building permits; Contracts
- Licenses, Insurance, etc.
- List of business consultants and professionals
Budget
| Account | Startup | Year I | Year II |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income | . | . | . |
| Personal Funds | $5000 | . | . |
| Sales | $2000 | $15,000 | $30,000 |
| Expenses | . | . | . |
| Costs and Supplies | $2000 | $5000 | $7000 |
| Salary | $5000 | $10,000 | $23,000 |
Assemble Resources
- Based on Research and Planning
- Board Members
- Management
- Staff
- Funding & Resources
- Initial
- Development Plan
Crowdfunding
- Internet-facilitated fundraising
- Tax Laws still apply
- Charitable Solicitation Laws still apply
- Take account of costs and fees (3-15%)
- Equity, Loan, Gift
- Entrepreneur: wider exposure, risk loss of ideas or control
- Investor: many ideas, lack of due diligence
Establish the Legal Foundations
- Increasing burden of inter-related legal regulation
- Cost of these mistakes
- An attorney familiar with nonprofit law is an indispensable help in successfully meeting all these demands
- File with the State:
- Articles of Incorporation
- Articles of Organization
- Register a Partnership
- Draft operating document:
- Bylaws
- Operating Agreement
- Partnership Agreement
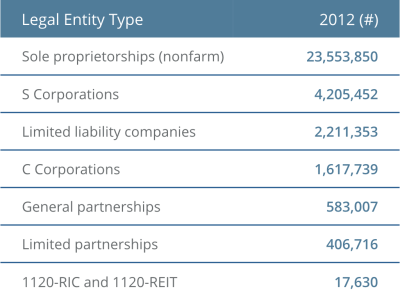
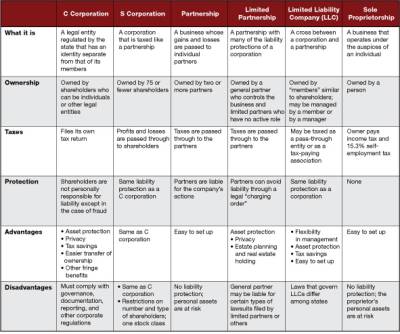
Forms of Ownership
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnerships
- General
- Limited
- Corporations
- Regular Corporation
- Subchapter S Corporation
- Limited Liability Company
Choosing a Form
- Organizational costs
- Limited versus unlimited liability
- Continuity
- Transferability of ownership
- Management control
- Raising new equity capital
- Income taxes
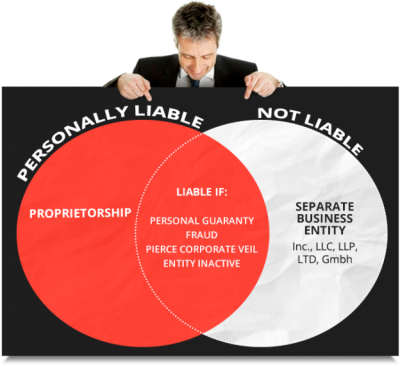
Sole Proprietor
- A sole proprietorship is a business owned and operated by one person.
- There is generally no registration or filing fee.
- Liability is unlimited.
- The sole proprietorship is dissolved upon the proprietor’s death.
- Ownership of the company name and assets may be transferred.
- Management freedom is absolute.
- Capital is limited to the proprietor’s personal capital.
- Income from the business is taxed as personal income to the proprietor.
Checklist
- Business Name
- Decide on a Name
- Research for others using that name
- Consider fictitious name or DBA
- Consider Trademark Registration
- Set up for
- State Sales tax
- Personal State and Federal tax
- Estimated Tax Withholding
- Set up a Finances
- Accounting
- Payment / Creditcard / Invoicing
- Bank accounts
- Arrange for pension
- Obtain all necessary business licenses
- Obtain apppropriate insurance
- Establish relationships with professionals
- Business attorney
- Accountant
- Develop a checklist for ongoing Legal Compliance
Liability
Partnership
- A partnership is a voluntary association of two or more persons to carry on, as co-owners, a business for profit.
- There is generally no registration or filing fee.
- Liability is unlimited.
- Unless the partnership agreement specifies otherwise, the partnership is dissolved upon withdrawal or death of a partner.
- Transferring ownership requires the consent of all partners.
- A majority vote of partners is required for control.
- Capital is limited by the partners’ ability and desire to contribute.
- Income from the business is taxed as personal income.
Limited Partnership
- Limited Partners invest in your business but are not otherwise active
- A written certificate must be filed with proper state office.
- Liability is limited to investment for limited partners.
- Withdrawal or death of limited partners does not affect the continuity of the business.
- Limited partners may sell their interest.
- Limited partners are not permitted any involvement in management.
- Limited partners’ limited liability provides a strong inducement in raising capital.
- Income from the business is taxed as personal income.
Checklist
- Name
- Decide on a Name
- Research for others using that name
- Consider fictitious name or DBA
- Consider Trademark Registration
- Set Up Partnership
- Record Partners names, ID#'s, record of ownership
- Set up partnership agreements
- Set up buy/sell - change in partnership interest agreements
- Establish contributions, payments, accounting, taxes for partners
- Establish
- Federal Tax ID#
- State Tax ID#
- State Sales Tax ID#
- State Unemployment, Withholding Tax ID#
- Apply for required operating permits, licenses, bonds, etc.
- Set up a Finances
- Establish appropriate accounting methods (tax year, cash vs. accrual, etc.)
- Set up acceptable bookkeeping system
- Establish expence procedures
- Set up bank / checking accounts
- Purchase Insurance
- Employees
- Personnel procedures / manual
- Establish Payroll procedures
- Establish relationship with professionals
- Bank
- Attorney
- Accountant
- Consider a business pension plan
- Develop a checklist for ongoing Legal Compliance
Partnership Agreement
- Name, Business and Location
- Term
- Capital - Contribution and ownership.
- Profit and Loss - How it is shared.
- Salaries and Drawings - No salary, but can draw on partner credit.
- Interest. No interest.
- Management Duties, Restrictions and Decisionmaking.
- Banking.
- Books. Accounting, access and fiscal year.
- Voluntary Termination. Distributions on termination to pay outstanding liabilities and obligations, then distribute to partners.
- Death.
- Disputes and Choice of Law - Any controversy or claim arising out of or relating to this Agreement, or the breach
Corporation
| Articles of Incorporation | Bylaws | EIN SS-4 | Licenses |
Articles of Incorporation and Bylaws
Articles of Incorporation
- Gives the organization a separate legal existence
- Filed with Secretary of State
- Generally a fill in form, but care must be taken in drafting purpose clauses
- Agreement with the state to establish and maintain the corporation: name, duration, location, registered agent, purpose, stock, amendment & dissolution
- Regular filing responsibilities, often overseen by secretary or treasurer
Bylaws
- Law for the Corporation
- Board Governance
- Purpose
- Board qualifications, terms and succession
- Board powers and responsibilities, meaningful oversight of staff – purposes, activities, financials
- Meetings, notice, decisionmaking
- Reporting requirements
- Financial structure
- Officers qualifications, terms and succession
- Committees
- Amendment and dissolution
Subchapter S Corporation
- It is taxed as a partnership.
- Eligibility requirements are as follows:
- No more than 75 stockholders are allowed.
- All stockholders must be individuals or qualifying estates and trusts.
- Only one class of stock can be outstanding.
- The corporation must be a domestic one.
- No nonresident alien stockholders are permitted.
- The S corporation cannot own more than 79 percent of the stock of another corporation.
- Benefits
- Tax Savings. No double tax
- Business Expense Tax Credits. Some business expense writeoffs.
- Independent Life. Keeps Business separate from life.
Checklist
- Name
- Decide on a Name
- Research for others using that name
- Consider fictitious name or DBA
- Consider Trademark Registration
- Set Up Corporation
- File Articles of Incorporation
- Adopt Bylaws for the Corporation
- Determine who will be Directors and Officers
- Set up and issue Stock
- Establish Corporate Minutes books
- Set up shareholder agreements (if more than one active owner)
- Set up buy/sell stock redemption agreement
- Arrange for any asset / liability transfers to corporation
- Apply for Subchapter S, if applicable
- Establish
- Federal Tax ID#
- State Tax ID#
- State Sales Tax ID#
- State Unemployment, Withholding Tax ID#
- Apply for required operating permits, licenses, bonds, etc.
- Set up a Finances
- Establish appropriate accounting methods (tax year, cash vs. accrual, etc.)
- Set up acceptable bookkeeping system
- Establish expence procedures
- Set up bank / checking accounts
- Purchase Insurance
- Employees
- Personnel procedures / manual
- Establish Payroll procedures
- Establish relationship with professionals
- Bank
- Attorney
- Accountant
- Consider a business pension plan
- Develop a checklist for ongoing Legal Compliance
Develop a Corporate Record-keeping System
- Records System
- Board, Management and Staff Records
- Finanical records
- Management
- Compliance (tax, grants, etc)
- Record Creation and Use
- Access and confidentiality
- Storage
- Security
- Record Retention and Destruction
- Legal implications
- When and How
State and Local Requirements
- Income Tax (state)
- Sales Tax (state and local)
- Property Tax (local)
- Franchise Tax, etc. (state and local)
- Licenses
Missouri
- Articles of Incorporation (SOS)
- Apply for sales tax ID from the state (DOR)
- Annual Report (SOS) (AG)
Local Regulatory Issues
- Business licenses and permits
- Licensing and insurance of professionals
- Business license
- Check Secretary of State website
- Zoning laws and municipal regulations
- Check city, county, municipal offices for necessary permits, regulations, zoning issues.
Employment and Payroll
- Federal Employment Laws
- State Employment Laws
- Industry Employment Requirements
- Payroll
- Exempt vs Nonexempt Employees and Overtime
- Withholding Accounting and Payment
- Employment Handbook
Intellectual Property
- Offensive and Defensive
- Trademark exclusively identifies the source or origin of products or services
- Copyright is a set of exclusive rights regulating the use of a particular expression of an idea or information
- Patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by a state for a fixed period of time which is new and useful
Checklist for Corporate Legal Compliance
- Board Meetings and Minutes
- Annual Filings
- Federal Tax
- State Corporate filings
- State Tax
- Permits, licenses
- Municipal filings and tax
- Financial and Audit Requirements
- Employment
- Contracts and Insurance
Policies and Procedures
- Staff Policies and Procedures
- Staff Record Management Policies and Procedures
- Staff Budget and Financial Policies and Procedures
- Employment Policies
- Staff Training Policies
- Client Services Policies and Procedures
- Character of Policies and Procedures
- Clear, useable and available to staff
- Managerial and organizational
- Drafted to anticipate and prevent legal problems.
Establish Financial Systems
- Develop an accounting system and budget.
- Gone are the days of shoe box accounting.
- Professional help in this area is important.
- Board Financial Management must ensure appropriate
- Oversight, recordkeeping and reporting.
Find a Site and Plan to Begin Operations
- All the hard work begins to pay off in services offered to clients.
- Ensure Policy / Procedures Compliance
- Ensure Recordkeeping
- Regularly review operations
- Update policies and procedures as required
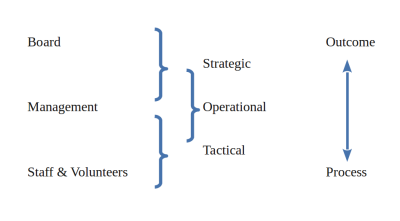
Legal Duties
- Duty of Care: Take reasonable care when making decisions for the organization, be competent
- Duty of Loyalty: Act in the best interest of the organization, confidentiality
- Recusal: Stand aside when there is a conflict of interest
- Duty of Obedience: Act in accordance with the organization’s mission, public trust
Board Governance
LLC
Limited Liability Company
- Limited liability for owners
- Taxed as a partnership
- Easier to establish, manage and control than corporations
- Now in all 50 states
- Limited transfer of ownership
- May be cumbersome to share or transfer ownership (unanimous written consent)
Checklist
- Name
- Decide on a Name
- Research for others using that name
- Consider fictitious name or DBA
- Consider Trademark Registration
- Set Up LLC
- File Articles of Organization with the State
- Adopt operating agreement
- Agree on ownership, capital contribution, profit-sharing
- Establish
- Federal Tax ID#
- State Tax ID#
- State Sales Tax ID#
- State Unemployment, Withholding Tax ID#
- Apply for required operating permits, licenses, bonds, etc.
- Set up a Finances
- Establish appropriate accounting methods (tax year, cash vs. accrual, etc.)
- Set up acceptable bookkeeping system
- Establish expence procedures
- Set up bank / checking accounts
- Purchase Insurance
- Employees
- Personnel procedures / manual
- Establish Payroll procedures
- Establish relationship with professionals
- Bank
- Attorney
- Accountant
- Consider a business pension plan
- Develop a checklist for ongoing Legal Compliance
Operating Agreement
- Introductory matters: formation, regulation of internal affairs, limitation of authority of a member, power to contract debts, use of legal company name, registered office/agent, record-keeping
- Start-up matters: maintenance of record book, establishment of bank accounts, reimbursement for organizational expenses, and LLC certificate
- Members: initial members, capital contributions and withdrawals, membership interests, admission of additional members, certificates of membership interest, and limitations of member liability and responsibility
- Management and control of the business including elections, annual/special meetings, officers, managers, and powers
- Capital accounts
- Allocations of net profits, net losses, and distributions
- Accounting, records, and reporting
- Transfer and assignment of interest
- Dissolution, winding up, and disassociation events
- Indemnification
Six Agreements
1. Operating Agreement / Bylaws
- identification of the owners;
- board of directors;
- voting rights;
- allocation of profits and losses;
- meeting times and places,
- owners' rights and obligations;
- addition of new owners;
- the right to sell or transfer stock or membership interests, and
- amendment and dissolution
2. Buy / Sell Agreement
- value of the company;
- family members able and willing to succeed;
- compensation of non-involved partners/family;
- income for spouse/dependent children;
- transfer of ownership outside partners/family;
- tax planning;
- funding; and
- when, why, how quickly
3. Contracts with vendors and customers
- goods/services,
- price,
- timeline,
- payment terms,
- breach and remedies.
4. Promissory notes, guarantees, security, releases
5. Corporate Minutes
- attendees,
- reports,
- elections of officers,
- resolutions
6. Non-compete, Non-disclosure, Confidentiality
- subject matter,
- geographic scope,
- timeframe,
- breach and remedies
Dissolution & Winding Down
- Close the Business As Required your Organizing Documents
- File with the State
- Notify the IRS and State and Local Tax Agencies
- Plan the Closing of Operations
- Cancel Business Licenses
- Terminate Contracts
- Notify Customers / Clients
- Liquidate Stock, Supplies and Equipment
- Plan staffing / severance
- Notification to Creditors
- Settle Creditor Claims
- Collect Money Owed to the Business
- Inform Other Stakeholders About the Closure
- Sell and Distribute Your Assets
- Meet with a Business Attorney Before You Dissolve Your Business